The hierarchy of courts of Malaysia starts with the Magistrates Court as the first level followed by the Sessions Court High Court Court of Appeal and the Federal Court of Malaysia which is the highest level. In this article we explain how you as a party to court proceedings can.
Nov 2018 An Introduction To The Malaysian Parliamentary System The Malaysia Culture Group
16 October 2013.

. Article 121 Part IX of the Federal Constitution. The hierarchy of courts of Malaysia starts with the Magistrates Court as the first level followed by the Sessions Court High Court Court of Appeal and the Federal Court of Malaysia. Article 121 of the Constitution of Malaysia provides that there shall be two High Courts of coordinate jurisdictionthe High Court in Malaya and the High Court in Sabah and Sarawak before 1994 the High Court in Borneo.
The Malaysian Court System. The Federal Court of Malaysia in the highest court of the land. Court System in Malaysia.
The Malaysian Court structure is greatly influenced by the English Court system and is divided into the Subordinate Courts and the Superior Courts. Like England Malaysia has its own Apex Court known as the Federal Court. The lowest level of the Subordinate Courts is.
The court system in Malaysia has been frequently criticised because of its dilatoriness in resolving disputes and resulted in back-log of cases. The Federal Court- as the highest court of the country. The High Courts in Malaysia are the third-highest courts in the hierarchy of courts after the Federal Court and the Court of Appeal.
In Malaysia a court hierarchy exists in the civil and criminal court system where there are different scopes of jurisdiction at each level. The Court of Appeal is the highest court of appeal on matters decided by the High Court in its appellate or revisionary jurisdiction. Article 121 of the Constitution of Malaysia provides that there shall be two High Courts of coordinate jurisdictionthe High Court in Malaya and the High Court in Sabah and Sarawak.
By Raymond Mah and Stella Lau. The criminal cases do not include cases involving the death penalty. The High Court Court of Appeal and the Federal Court are superior courts while the Magistrates Court the Court for Children and the Sessions Court are subordinate courts.
No Mr Justice Peter cannot decline to be bound by the decision of Court of Appeal. This article will aim to break down the essential elements and rules. The Court of Appeal is limited to only perform the function of an Appellate Court.
One of the reasons is because the court system in Malaysia is practicing a judicial precedent. Although Singapore left Malaysia in 1965 the High Court of Singapore remained part of the Malaysian Judicial System until the Supreme Court of Singapore was reintroduced in 1969. Judicial precedent is a previous judicial decision or preceding that may adopted by the judges.
It is created by the English judges and introduced into Malaysia upon colonization. The Magistrates Court the Court for Children and the Sessions Court are subordinate courts. Article 121 of the Constitution of Malaysia provides that there shall be two High Courts of coordinate jurisdictionthe High Court in Malaya and the High Court in Sabah and Sarawak before 1994 the High Court in Borneo.
Before 1969 the High Court in Singapore was also part of the Malaysian courts system see Law of Singapore. The current numbers of Judicial Commissioners as of April 2016 is 37 out of which 33 judges are posted in High. The Privy Council appeals were allowed on criminal and constitutional matters only until 1 January 1978 while the appeals for civil matters were abolished on 1 January 1985.
Similar to England our second Highest Court. The Magistrate Court has jurisdiction to try civil cases whose claim does not exceed RM 25000. Sessions Courts has the authority to decide on civil and criminal cases.
The Federal Constitution does not limit the number of judicial commissioners to be appointed in the two High Courts of Malaysia. It is the second highest court in the judiciary system in Malaysia. MahWengKwai Associates offers you an insight into the Malaysian Courts Electronic Filing System also known as the e-Filing System or EFS in short with answers to some frequently asked questions FAQs.
Before 1969 the High Court in Singapore was also part of the Malaysian courts system see Law of Singapore. The system of binding judicial precedent is called stare decisis. It also has jurisdiction to try cases whose maximum penalty does not exceed 10.
The term jurisdiction will come up often but all it means is the authority of a court to hear and determine cases. The superior court system of Malaysia has a three-tier superior court system. The Federal Court serves the same function as the Supreme Court of England or fondly remembered as the House of Lords in that it is the highest appellate court that can hear appeals of civil and criminal cases.
Glossary of Common Civil Litigation Terms Retrieved November.

Russian Police Hierarchy Hierarchical Structure And Charts

Legal Services In Malaysia Law Firm Legal Services Concord

Victoria Police Hierarchy Hierarchy Structure

Hierarchical Structure Of The Ordinary Courts Download Scientific Diagram
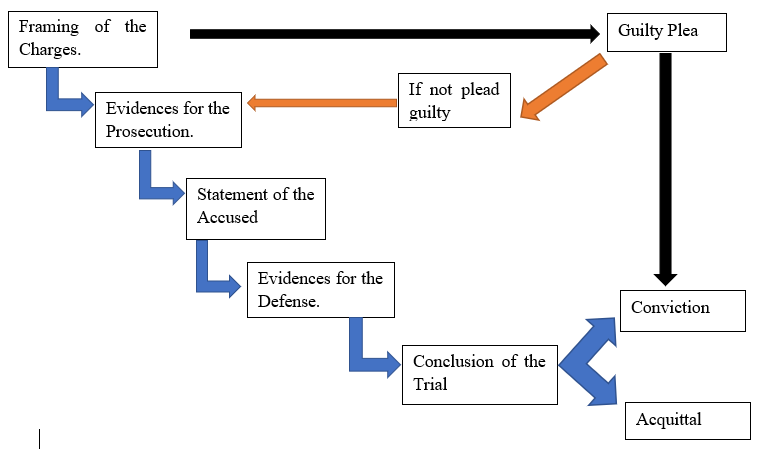
Trial Stage In Criminal Law Ipleaders

The Abolishment Of Jury System In Malaysia Alsa Malaysia
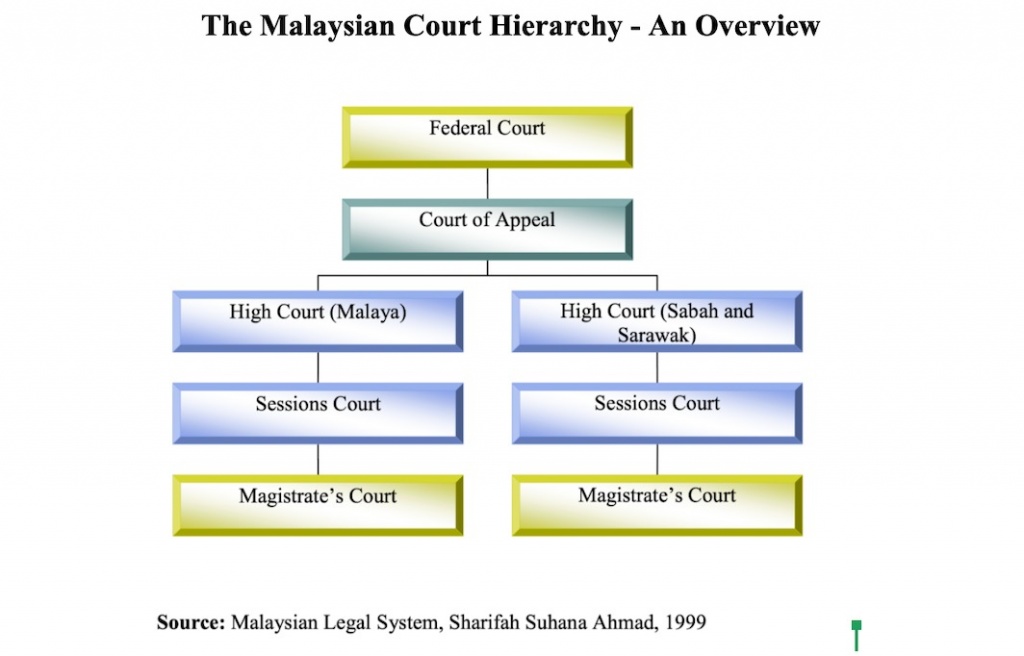
The Malaysian Court Hierarchy A Review Of Malaysia S Civil And Criminal Court Hierarchy Richard Wee Chambers
Nov 2018 An Introduction To The Malaysian Parliamentary System The Malaysia Culture Group

The Malaysian Court System Asklegal My
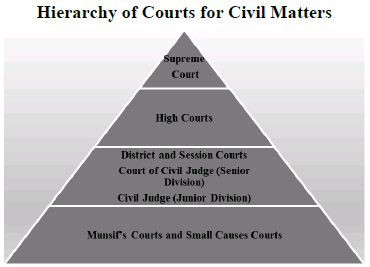
Hierarchy Of Courts For Civil Cases In India Civil Law India

Chicago Police Hierarchy Structure Police Ranks

British Police Hierarchy System Hierarchy Structure

Police Hierarchy In Sri Lanka Hierarchystructure Com

You Can Make An Appeal If You Lose Your Case In Asklegal My

Hierarchical Structure Of The Ordinary Courts Download Scientific Diagram

The Malaysian Court System Asklegal My
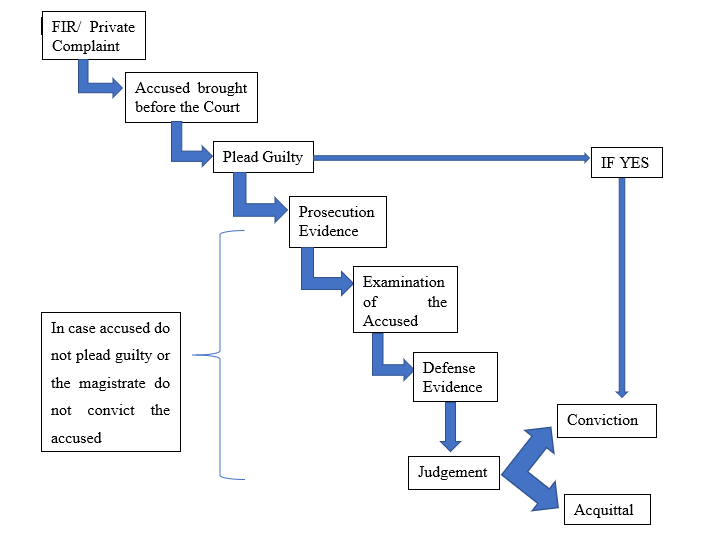
Trial Stage In Criminal Law Ipleaders
Advantages Of Court Hierarchies

